You Are Viewing
Neuropathy Entrapment
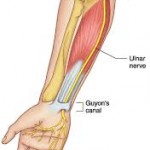
Pain, loss of strength or sensory changes in the distribution of the median or ulnar nerves but not associated with neck pain.
 Neuropathy Entrapment: Initial Diagnosis and Management
Neuropathy Entrapment: Initial Diagnosis and Management
- History and physical examination for neuropathy entrapment.
- Plain radiographs are not required.
- NSAIDs.
- Adults – 200 to 400 milligrams (mg) every four to six hours as needed for up to 2 weeks. Example: Ibuprofen
- Take tablet or capsule forms of these medicines with a full glass (8 ounces) of water.
- Do not lie down for about 15 to 30 minutes after taking the medicine. This helps to prevent irritation that may lead to trouble in swallowing.
- To lessen stomach upset, these medicines should be taken with food or an antacid for neuropathy entrapment.
- For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome symptoms prescribe a volar wrist splint to wear at night and during the day (take splint off every 2 hours and move wrist to prevent stiffness). Also avoid activities that promote symptoms.
- For cubital tunnel syndrome, educate the patient to avoid pressure on elbow and to avoid activities that increase symptoms. Refer to Occupational Therapy for night elbow splints.
Neuropathy Entrapment: Ongoing Management and Objectives
- Expect Resolution or decreasing symptoms within three to four weeks.
Neuropathy Entrapment: Indication a profile is needed
- Any limitations that affect strength, range of motion, and general efficiency of upper arms.
- Slightly limited mobility of joints, muscular weakness, or other musculo-skeletal defects that may prevent hand-to-hand fighting and disqualifies for prolonged effort.
- Defects or impairments that require significant restriction of use due to neuropathy entrapment.
Neuropathy Entrapment: Specifications for the profile
- Week 1-4
- No upper body PT requiring flexion or extension at the wrist
- No lifting or pushing with affected wrist
- No low crawl
- No stretcher duty with affected wrist(s)
- Motor vehicle driving only with splint and with caution for neuropathy entrapment.
 Neuropathy Entrapment: Initial Diagnosis and Management
Neuropathy Entrapment: Initial Diagnosis and Management